[10000ダウンロード済み√] gravitational constant formula class 9 458828-Gravitational constant formula class 9
According to the universal law of gravitation,gravitational force exerted on an object of mass m is given by Where, Mass of Earth, M = 6 x 10 24 kg Mass of object, m = 1 kg Universal gravitational constant, G = 67 x 10 11 Nm 2 kg 2 Since the object is on the surface of the Earth, r = radius of the Earth (R) r= R = 64 x 106 mUniversal gravitational constant, G = 67 × 10 −11 Nm 2 kg −2 Since the object is on the surface of the Earth, r = radius of the Earth (R) r = R = 64 × 10 6 mThe formula of gravitation can be stated as F = G * (m1*m2)/R2 In this gravitational force equation F → Magnitude of the gravitational force G → It is the gravitational constant and its size depends on the system of units used m1, m2 → Masses of the two objects R Distance between the masses

Cbse Class 9 Science Chapter Gravitation Notes Part I
Gravitational constant formula class 9
Gravitational constant formula class 9-The relation between Universal Gravitational Constant G and Gravitational Acceleration g is also important for terminal exams or class test Chapter 10 of Class 9 Science also states about the difference between Mass and Weight considering the values of gThe acceleration of free fall is;




Calculate The Mass And Mean Density Of The Earth From The Followin
Mar 02, 19 · The gravitational constant, denoted by the letter G, is an empirical physical constant involved in the calculation of gravitational effects in Sir Isaac Newton's law of universal gravitation and in Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity Wikipedia Formula G= \times 10^{11} \;Oct 02, 19 · Gravitational constant is numerically equal to the force of attraction between two masses of 1 kg that are separated by a distance of 1 m 2 G is a scalar quantity 3 The 'G' is a universal constant, ie, its value is the same (ie 67 × 10 11 Nm 2 kg 2) everywhere in the universe Question 4Dec 15, 19 · The formula for the magnitude of gravitational force between the earth and an object on its surface is, where F is the gravitational force G is the gravitational constant M e is the mass of the earth m is the mass of the object on the surface of the earth If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10
Calculation of value of g G = 667 × 10 –11 Nm 2 /kg 2 M = 6 × 10 24 kg (Mass of the earth) R = 64 × 10 6 m On substituting the given values Motion of objects under the influence of gravity 'g' does not depend on the mass of the body All objectsEarth's Normal Gravity at the Equator LIGHT_SPEED Velocity of light in vacuum e8 MEAN_NORMAL_GRAVITY Earth's Mean Normal Gravity NORMAL_GRAVITY_FORMULA Constant for Normal Gravity Formula e3 NORMAL_GRAVITY_POTENTIAL Earth's Normal Gravity PotentialUnits And Dimensions of Class 11 The dimension of a physical quantity are the powers to which the fundamental (or base) quantities like mass, length and time etc have to be raised to represent the quantity Consider the physical quantity "Force" The unit of force is Newton 1
Aug 28, · Gravitation Class 9 Extra Questions Short Answer Type 1 Question 1 Write down SI unit of (a) Universal gravitational constant (b) Acceleration due to gravity (c) Density (d) Relative density (e) Mass (f) Weight Answer (a) Nm2/kg 2 (b) rn/s 2 (c) kg/m 3 (d) no unit (e) kg (f) N Question 2 If an iron ball exerts a gravitational force F onJan 15, · The acceleration produced in freely falling body due to gravitational force is called acceleration due to gravity Acceleration due to gravity is represented by letter 'g' Value of g is 9Dec 17, · In the above equation, 'G' is the Gravitational Constant The dimension formula of gravitation constant is M1L3T2, and the units and respective values of the gravitational constant are Test your knowledge with our Physics quiz !




What Is The Relationship Between G And G Quora




Ncert Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Exercise
Jun 23, 17 · Online test of Chapter 10 Gravitation 1 Class 9th Science Questions 1 What is the centripetal force that makes moon revolve around earth?G The universal Gravitational constant The value of the proportionality constant that is the value of the universal gravitation constant is found to be G = 6673 x 1011Nm2/kg2 Equation (4) is known as the mathematical form of Newton's law of gravitation or the law of gravitational force From equation (4) we find that the force acting onJan 18, 19 · Answer Let the mass of two interacting bodies be m 1 and m 2 and d be the distance between them, then the force of gravitation/gravitational force is given by latexF=G\cfrac { { m }_ { 1 } { m }_ { 2 } } { { d }^ { 2 } } /latex where G is called gravitational constant Question 12




Universal Law Of Gravitation Class 9 Physics Gravitation Youtube




Newton S Laws And Weight Mass Gravity Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Gravitational constant and its units According to the law The value for G is always the same at all places If we need to define gravitational constant, then, we have to take all values as unity except G that is Consider two bodies of masses 1 kg each separated by distance 1 m, then the expression becomes G=F x (1)2/1 x 1 So, we can define G asLakhmir Singh Physics Class 9 Solutions Page No100 Question 1 What is the value of gravitational constant G (i) on the earth, and (ii) on the moon ?Class 9 CBSE Unit of Gravitational ConstantChapter Gravitation Easy than Learn




Derive Formula Of Universal Law Of Gravitation Brainly In



What Is The Relation Between G And G Gravitation Science Class 9
May , · Value of universal gravitational constant, G = 67 × 10 –11 N m 2 / kg 2, Mass of the earth, M = 6 × 10 24 kg, and Radius of the earth, R = 64 × 10 6 m Putting all these values in equationAug 31, · MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science Ch 10 Gravitation 1 The earth and the moon are attracted to each other by gravitational force The earth attracts the moon with a force that is (a) More than that exerted by the moon (b) Same as that exerted by the moon (c) Less than that exerted by the moonThe gravitational field strength g describes the amount of force exerted upon every kilogram of mass in the location surrounding a massive planet, star, or any object (including a person) that has mass It describes the strength of the gravitational forces that a massive object exerts at any location around it Its value can be quantitatively described by an equation that derives from



Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation




Calculating Acceleration Due To Gravity Formula Concept Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
When the Body falls due to earth's gravitational pull, its velocity changes and is said to be accelerated due to the earth's gravity and it falls freely called as free fall This acceleration is calculated to be 98 m/s 2Where G is universal gravitational constant The value of G is 667 X 1011 Nm2 kg2 and is same throughout the universe The value of G is independent of the nature and size of the bodies well as the nature of the medium between them Dimensional formula of Gis M1L3T2 Important Points about Gravitation Force4 If Planck's constant (h ) and speed of light in vacuum (c ) are taken as two fundamental quantities, which one of the following can, in addition, be taken to express length, mass and time in terms of the three chosen fundamental qua ntities?




Calculating Acceleration Due To Gravity Formula Concept Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Newton S Universal Law Of Gravitation Physics
\frac{N \cdot m ^{2}}{ kg^{2}}Dec 06, 18 · 9 • The value of Universal Gravitational Constant G is 667 x 1011 N m2 Kg2 • The value of G does not depend on the medium between two bodies • The value of G is same throughout the Universe and hence the name(a) Gravitational Force (b) Electrostatic Force (c) Magnetic Force (d) None 2 The mass of an object is the measure of its (a) pressure (b) weight (c) inertia (d) thrust 3




Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 9 Solutions Chapter 3 Gravitation Learn Cbse




Ncert Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Exercise
Universal gravitational constant, G = 67 × 10−11 Nm2 kg−2 Since the object is on the surface of the Earth, r = radius of the Earth (R) r = R = 64 × 10 6 mThe type of gravity model used for the Earth depends upon the degree of fidelity required for a given problem For many problems such as aircraft simulation, it may be sufficient to consider gravity to be a constant, defined as = metres ( ft) per s 2 based upon data from World Geodetic System 1984 (), where is understood to be pointing 'down' in the local frame ofMay 17, 21 · The value of G is given by the following formula G = F d 2 M × m G = ( 98 × 10 – 7) × ( 02) 2 ( 40 × 15) ⇒ G = 6533 × 10 – 11 N m 2 k g – 2 Based on Newton's law of gravitation, we can conclude that the force of gravitation is a mutual




Cbse Class 9 Science Chapter Gravitation Notes Part I




Gravitational Acceleration Physics Problems Formula Equations Youtube
Sep 27, 15 · Science gravitation for class 9th 1 Gravitation Earth attracts everything towards it by an unseen force of attraction This force of attraction is known as gravitation or gravitation pull Universal Law of Gravitation Every object in the universe attracts other object by a force of attraction, called gravitation, which is directlySolution Value of gravitational constant G on the earth and the moon is = 667 x 10 11 Nm 2 /kg 2 Note that the value of G always remains constant irrespective of the locationIt contain all the physics formulas for class 9This PPT will help the students to learn physics formulas in an effective manner Universal Law of gravitaion F=GMm/d2 Where M=mass of A m=mass of B G=gravitational constant d=distance between A & B Free Ball g=GM/d2 where M=mass of A G=gravitational constant d=distance between A & B g




Calculate The Mass And Mean Density Of The Earth From The Followin




Gravitation Class 9
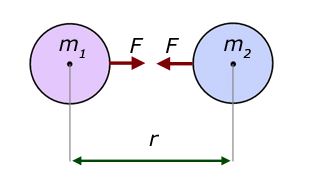
(9), namely, universal gravitational constant, G = 67 × 10 –11 N m 2 kg2, mass of the earth, M = 6 × 10 24 kg, and radius of the earth, R = 64 × 10 6 m g=G M/R 2 67 1011 N m 2 kg2 6 10 24 kg / (64 10 6 m) 2 = 98 m s –2 Thus, the value of acceleration dueAcceleration due to gravity, g is not a universal constant like G Its calculated by formula mentioned in previous answers So, for a constant mass system, g depends only on r (distance between center of earth & object in problem) As r = R h (R is radius of earth & h is height of object from surface) & R is constant, g depends mainly on heightThe gravitational force of attraction between two bodies is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them If two masses m 1 and m 2 are separated by a distance r then F ∝ \(\frac {m_{m2}}{r2}\) Or \(F =G\frac {m_1m_2}{r^2}\) Where G is the proportionality constant



Newton S Universal Law Of Gravitation Isaac Newton The Guardian




Gravity Equation F Force Of Gravity G Gravitational Constant 6 M 1 Mass Of Body 1 M 2 Mass Of Body 2 S 2 Distance Between Ppt Download
Aug 19, 19 · In physics, the value of capital G (gravitational constant) was initially proposed by Newton G = × 10 11 N m 2 Kg 2 The value of gravitational constant on the moon or on mars or at any part of the universe remains unchanged making it an invariant entityWhat is the dimensional formula of (a) volume (b) density and (c ) universal gravitational constant 'G' The gravitational force of attraction between two objects of masses m and m separated by a distance d is given by F = (G m_(1) m_(2))/(d^(2)) Where G is the universal gravitational constantAug 21, 17 · G is a constant and is known as Gravitational constant Value of G = 667×10 11 Nm 2 /kg 2 G is called universal gravitational constant → If unit of F is in Newton, m is in kg, d is in metre, then unit of G can be calculated as



1




Big G Scientists Pin Down Elusive Gravitational Constant Live Science
Two identical small balls each of mass m are rigidly affixed at the ends of light rod of length $$15\m$$ and the assembly is placed symmetrically on an elevated protrusion of width/ as shown in the figure The rodball assembly is tilted by a small angle $$\theata$$ In the vertical plane as shown in the figure and releasedVector Form of GravitationSep , 13 · G stands for Newton's universal gravitational constant, whereas g stands for the acceleration due to gravity at a certain point G = × 1011 Nm2kg2, G is a constant throughout space and time and it is a scalar quantity g = 98 ms2, g is acceleration due to gravity which is a variable quantity and a vector qualtity g is a




Cbse Class 9 Science Chapter Gravitation Notes Part I




Universal Gravitational Constant And Gravitational Acceleration Of
O O O O (a) (b) (c) (d) Mass of electron (me) Universal gravitational constant (G) Charge of electron (e)Three balls P, Q and R are kept in a straight line The separation between P and R is 1m, and Q is placed at the midpoint between them The masses of P, Q, R are 0 g, 300 g and 400 g respectively Find the net gravitational force on P, Q and R respectively Few characteristics of a quantity are given belowClass 9 Physics Notes Chapter 5 Gravitation Exercise G = gravitational constant = 6673×1011 Nm 2 kg2 Formula shows that orbital speed of a satellite depends upon g, R and h The orbital velocity of the satellite depends on its altitude above Earth The nearer the Earth, the faster the required orbital velocity




Cbse Class 9 Science Chapter Gravitation Notes Part I




Revision Notes For Science Chapter 10 Gravitation Class 9th Askiitians
May 15, 19 · Its value, G = 667 × 10–11 Nm2 kg–2 Dimensions of G are M–1 L3 T–2 The gravitational force is the central force and follows inverse square law It acts along the line joining the particles Since the work done by the gravitational force is independent of the path followed and hence it is a conservative force"K" is called electrostatic constant, it depends on the medium The value of 'K' in a vacuum medium, K = 9 x 10 9 Nm 2 /C 2 The formula of K in a vacuum, K = 1/4πε o Where ε o is known as permittivity of free space or vacuum ε o = 54 x 1012 C 2 /Nm 2 The formula of 'K' other than vacuum, K = 1/4πεApr 12, 17 · The Universal law of gravitation can be summed by this gravitational force formula F G = (Gm1m2)/r 2, where G is a constant which is known as Universal Gravitational Constant or Gravitational constant This equation gives us the expression of the gravitational force



Variation In Acceleration Due To Gravity Due To Lattitude Height And Depth
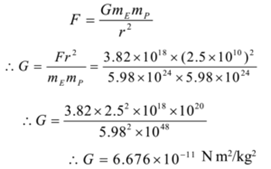



Gravitational Force Of Attraction Numerical Problems
The above equation is the mathematical representation of Newton's universal Law of gravitation Hence, G = Fr2/ m1 m2 SI Unit Nm2 kg2 Value of G = 6673 × 10 11 Nm 2 kg 2 (was found out by Henry Cavendish (1731 1810))



State And Explain Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation



What Is The Dimension Formula For A Gravitational Constant Quora
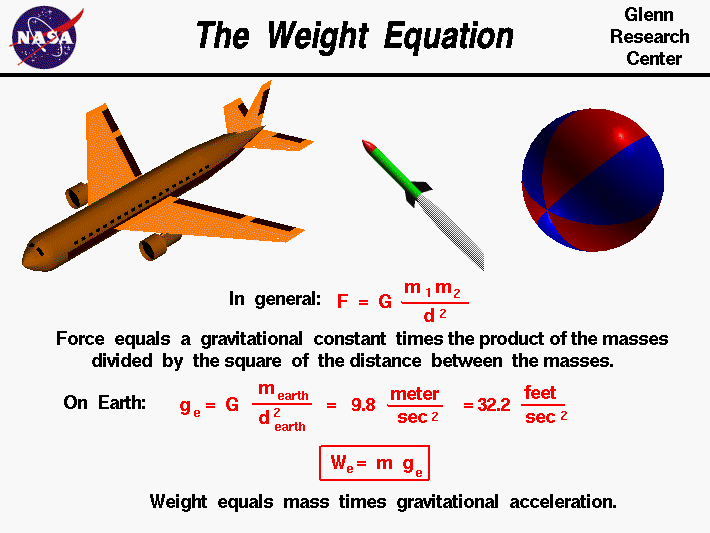



Weight Equation




Ncert Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation




Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation Wikipedia



1




Chap1 La Gravitation
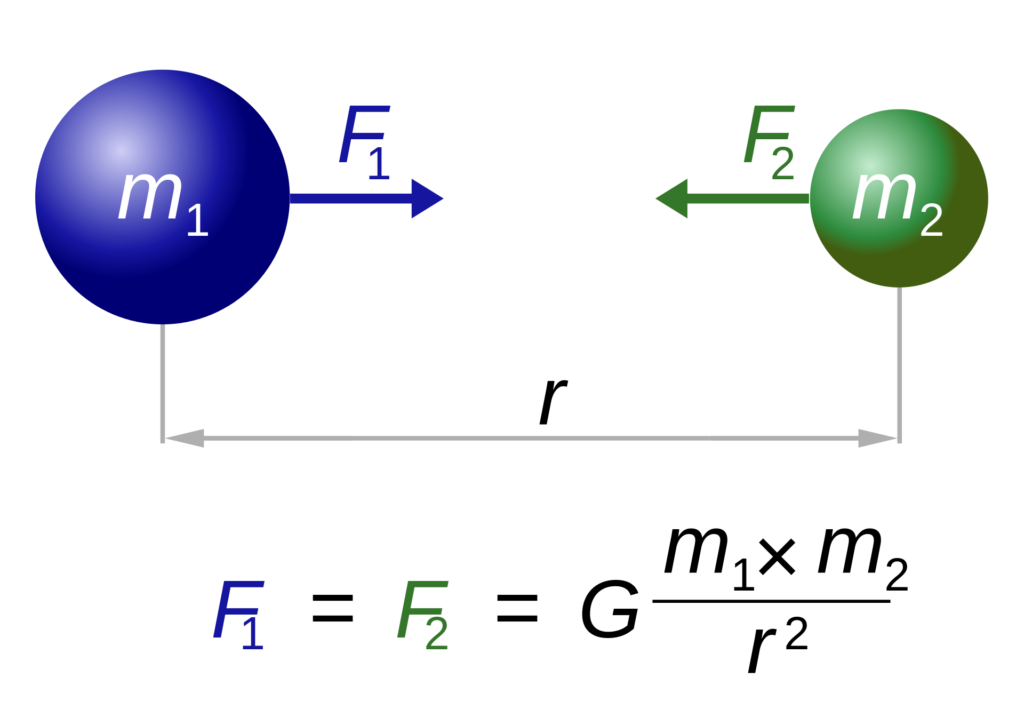



Gravitational Force Formula Definition Equations Examples




What Is Universal Law Of Gravitation Class 9 Gravitation Teachoo




Newton S Universal Law Of Gravitation Physics




Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 9 Solutions For Chapter 3 Gravitation Free Pdf



Cbse 9 Physics Cbse Gravitation Notes




What Is Universal Law Of Gravitation Class 9 Gravitation Teachoo




Introduction To Newton S Law Of Gravitation Video Khan Academy
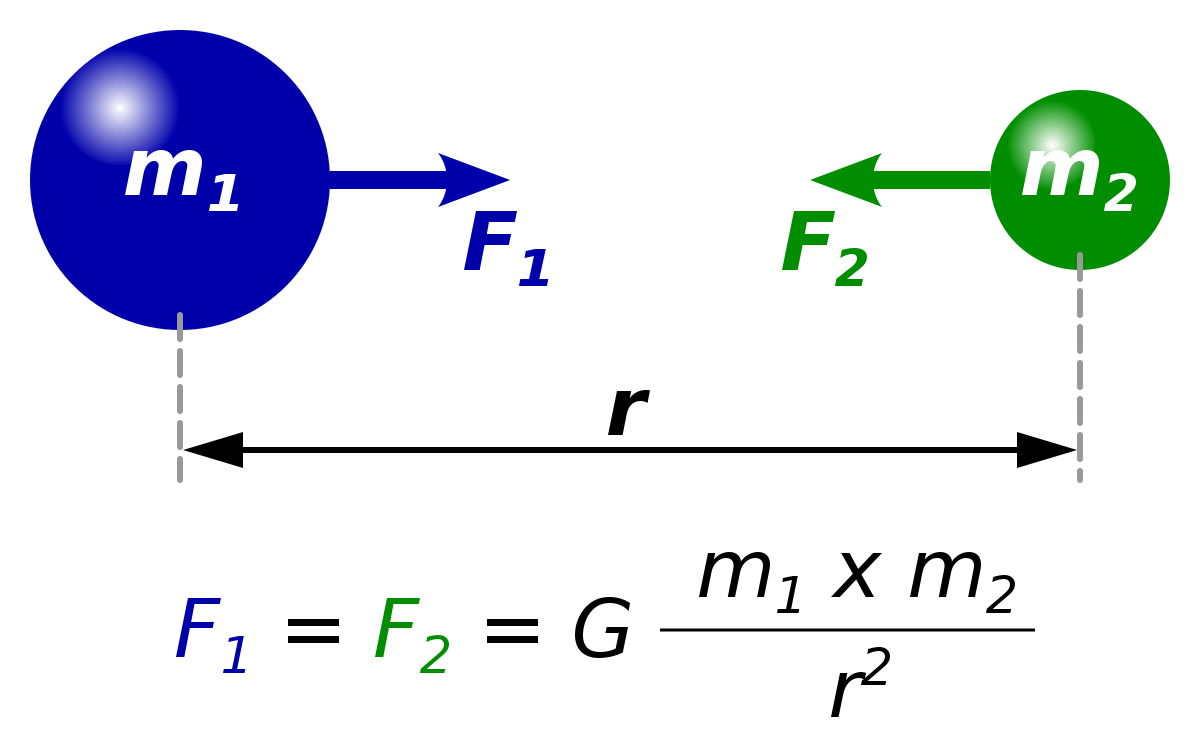



Gravitational Constant Wikipedia




Gravitation Class 9 Notes Science Chapter 11 Explanation Question Answers




Cbse Papers Questions Answers Mcq Cbse Class 9 Science Ch10 Gravitation Worksheet 1



What Is The Relationship Between Acceleration Due To Gravity And Mean Density In Terms Of The Gravitational Constant And The Radius Of The Earth Quora




Ncert Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation




Pin On Physics Notes Jee Neet



Derive A Mathematical Expression For The Newtons Law Of Gravitation Physics Topperlearning Com Mkqjr32qq
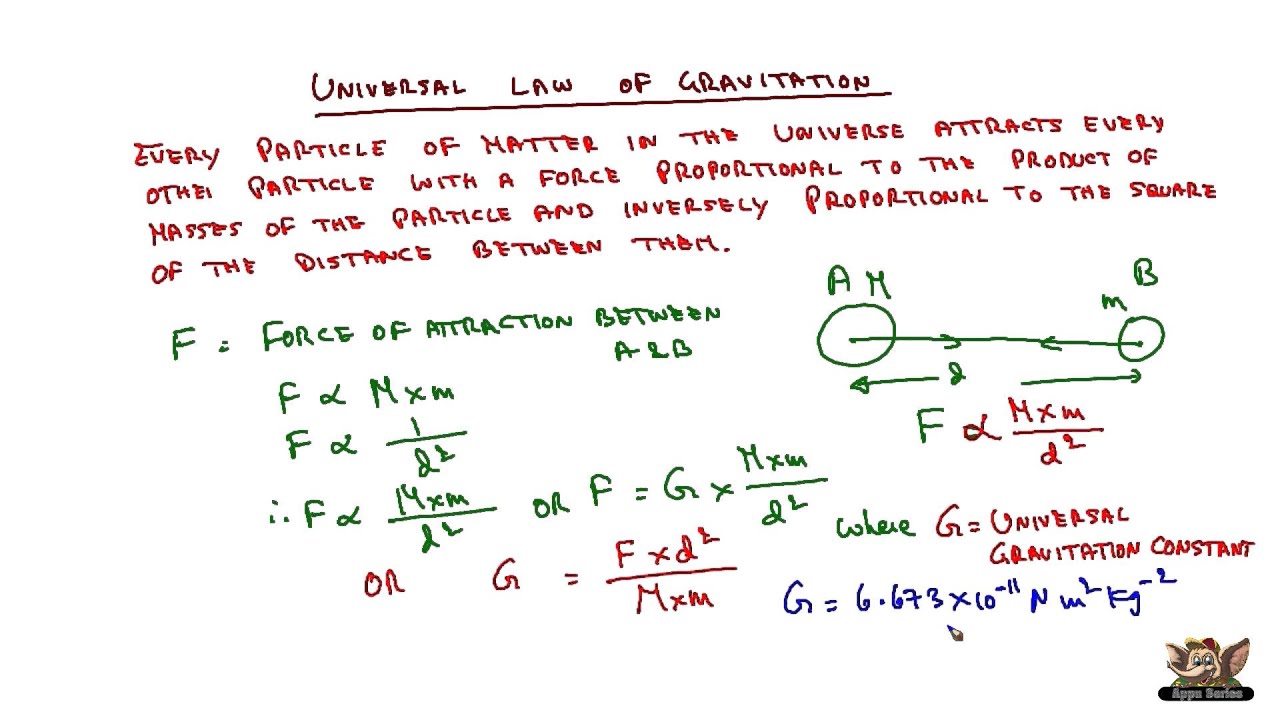



Universal Law Of Gravitation Youtube



Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation



1




What Is Free Fall And Acceleration Due To Gravity Teachoo




Gravity Newton S Law Of Gravity Britannica




Physics Formula For Class 9 Chapter Gravitation Entrancei




Universal Gravitational Constant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
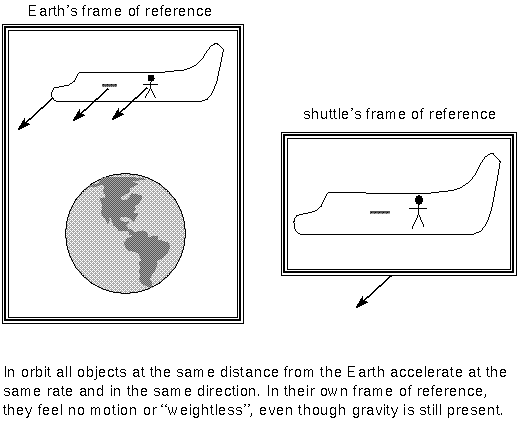



Gravity Applications




Universal Gravitational Constant Gravitation And Flotation Cbse Grade 9 Physics Youtube




How To Calculate Force Of Gravity 10 Steps With Pictures
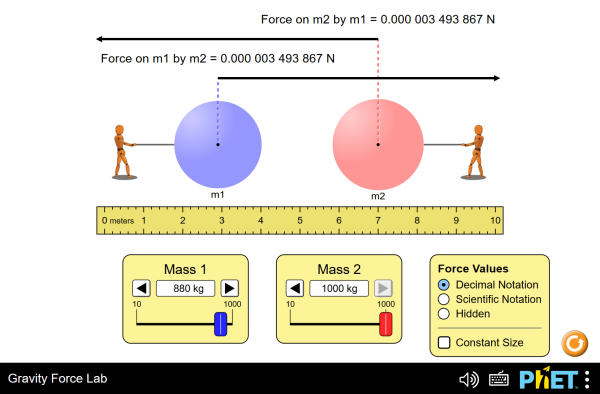



Gravity Force Lab




Notes Of Ch 10 Gravitation Class 9th Science




Falling For Gravity Physics Mathematics Science Activity Exploratorium Teacher Institute Project




Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 9 Solutions For Chapter 3 Gravitation Free Pdf




Viewing G As The Value Of Earth S Gravitational Field Near The Surface Video Khan Academy
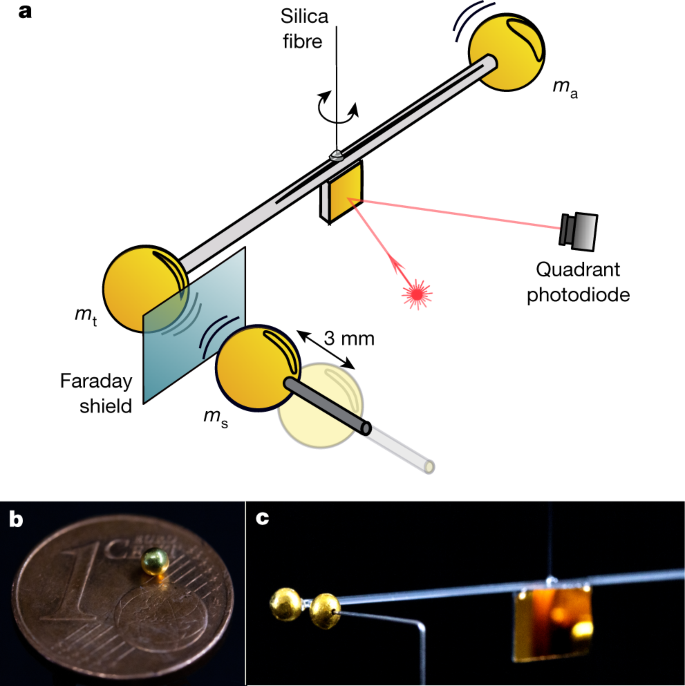



Measurement Of Gravitational Coupling Between Millimetre Sized Masses Nature




Define Acceleration Due To Gravity Derive An Expression For Acceleration Due To Gravity In Terms Of Mass Of The Earth M And Universal Gravitational Constant G Cbse Class 9 Science




All Formula Of Gravitation Chapter Class 9th Brainly In




1 We Showed In Class That For Any Fluid At Rest Chegg Com




Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 9 Solutions For Chapter 3 Gravitation Free Pdf



Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation
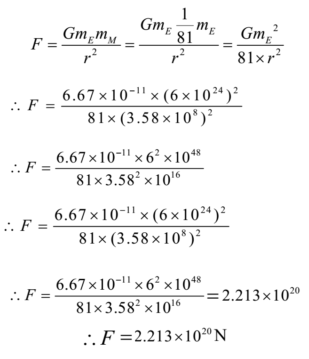



Gravitational Force Of Attraction Numerical Problems



1




Important Notes Of Physics For Neet Jee Gravitation




State And Derive The Formula For The Gravitational Force Of Attraction Between Sun And Earth Science Gravitation Meritnation Com



Introduction To Gravity Video Khan Academy
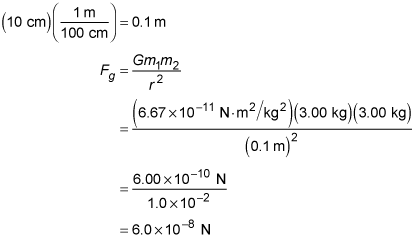



Gravitational Force In Physics Problems Dummies



Gravity Universal Gravitation Constant Gravitational Force Between Earth Moon Sun Physics Youtube




Acceleration Due To Gravity Formula Values Of G And Variations



Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation




Gravity Newton S Law Of Gravity Britannica




Isaac Newton S Formula For The Force Of Gravity Definition Example Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Learnhive Cbse Grade 9 Science Gravitation Lessons Exercises And Practice Tests




Ncert Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation Free Pdf



What Is The Dimension Formula For A Gravitational Constant Quora




Gravitational Constant Wikipedia
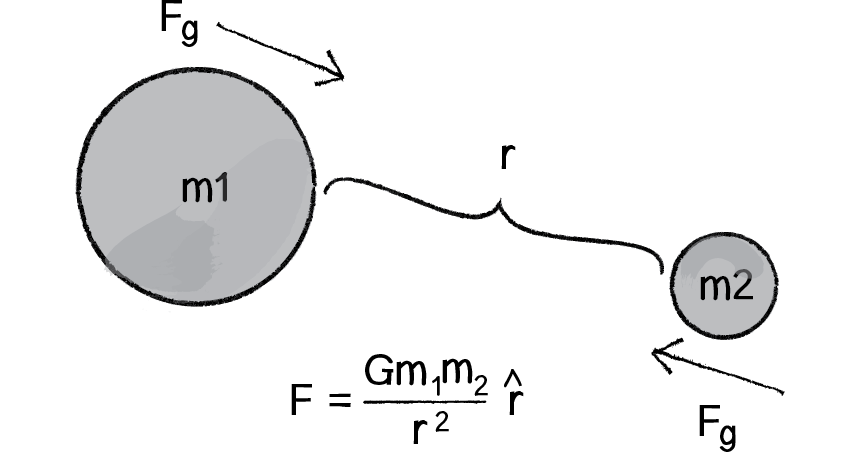



Gravitational Attraction Article Forces Khan Academy



Cbse 9 Physics Cbse Gravitation Ncert Solutions



Http Metasofsda In School Wp Content Uploads Sites 4 04 Physic Chapter 03 Exercise Solution Pdf




Derive Expression For Force Of Attraction Between Two Bodies And Then Define Gravitational Constant Cbse Class 9 Science Learn Cbse Forum




Acceleration Due To Gravity Formula Definition And Examples



Universal Law Of Gravitation Learn Physics Class 9 Amrita Vidyalayam Elearning Network




Pin On Swati S




Class 9th Physics Gravitation Acceleration Due To Gravity Youtube
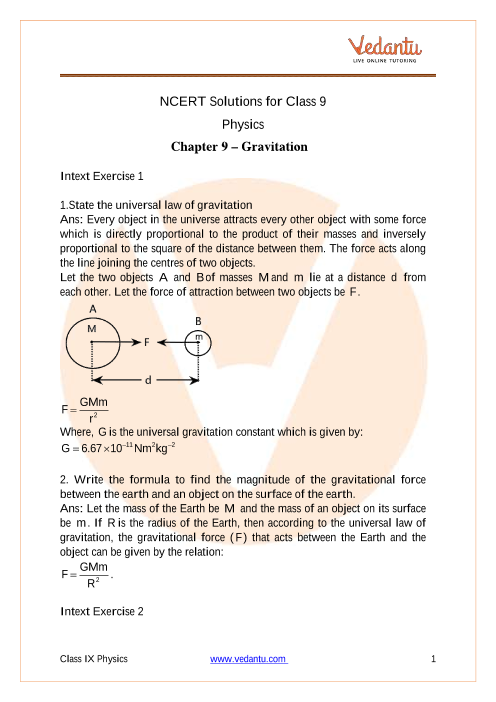



Ncert Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation Free Pdf




What Is Universal Law Of Gravitation Class 9 Gravitation Teachoo




Gravitational Force Calculator



Cbse Class 11 Physics Gravitation Notes Set A Concepts For Physics Revision Notes




Write All Formula Of Chapter 10 Gravitation Full Class 9 Only And Only Formula Brainly In




What Is Difference Between G And G




Newton S Universal Law Of Gravitation Concepts Videos And Questions
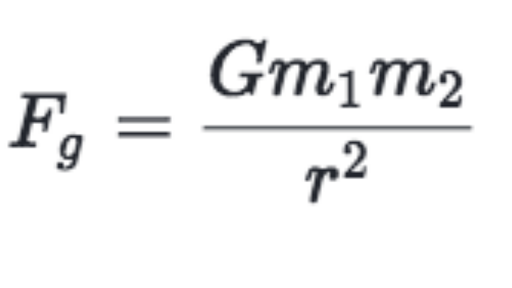



Newton S Law Of Gravitation Review Article Khan Academy



Sir Isaac Newton The Universal Law Of Gravitation



What Is Difference Between G And G




The Si Unit Of Gravitational Constant Is Youtube




280 Questions With Answers In Gravitation Science Topic




Cbse Class 9 Science Chapter Gravitation Notes Part I


コメント
コメントを投稿